In ancient Egypt, the Nile River flowed and the sun shone brightly. A group of gods and goddesses ruled over this land. They had special powers and meanings, building the foundation of the civilization.
Their stories and myths have amazed people for thousands of years. They shaped the beliefs and lives of those who worshipped them.
As you explore Egyptian mythology, you’ll learn about 10 key gods. These gods, like Ra and Anubis, have inspired awe and fear for generations.
Key Takeaways
- Explore the fascinating world of ancient Egyptian gods and goddesses
- Discover the unique powers, myths, and legacies of 10 influential deities
- Uncover the enduring impact of Egyptian mythology on culture and daily life
- Learn about the significance of animal symbolism in the Egyptian pantheon
- Gain a deeper understanding of the divine lineage and family tree of Egyptian gods
Discover The Egyptian Frequency That Transforms You Into A Wealth Magnet—In Just 24 Hours!
The Fascinating World of Egyptian Gods
Ancient Egypt was filled with a rich array of deities, each with their own powers and myths. These egyptian gods have fascinated scholars and the public for centuries. They help us understand the mysteries of this ancient civilization.
Uncovering the Mysteries of Ancient Egypt
The egyptian mythology is complex, showing the depth of Egyptian culture. Gods like Ra and Anubis were key in ancient Egyptian society. They played important roles in religion, politics, and daily life.
- Explore the intricate web of relationships between the various egyptian gods and their associated symbols, rituals, and mythological tales.
- Discover the ways in which these deities were revered and worshipped, and how their influence permeated every aspect of daily life in ancient Egypt.
- Delve into the symbolic and allegorical meanings behind the animal-headed figures, uncovering the deeper significance of these divine representations.
The Enduring Legacy of Egyptian Mythology
The egyptian mythology has captivated people worldwide, inspiring art and literature. The legacy of these egyptian gods shows the lasting impact of ancient Egyptian civilization.
“The gods of ancient Egypt continue to captivate the modern world, their mythological tales and symbolic representations a window into the rich and complex spiritual beliefs of a remarkable civilization.”
Ra: The Supreme Ruler of the Egyptian Pantheon
Ra was the top god in ancient Egypt, loved and respected by all. As the sun god, Ra’s power touched every part of Egyptian life. This included the seasons and their belief system.
The Sun God and His Powerful Influence
Ra was seen as the creator, sailing in his solar barque each day. He brought light and life to the world. The Egyptians saw him as the king of gods, the universe’s creator, and its sustainer.
They built big temples and monuments for Ra. They wanted his blessings and protection.
Myths and Legends Surrounding Ra
- The myth of Ra’s daily journey across the sky, where he battles the forces of darkness and chaos to bring the sun to the world each morning.
- The legend of Ra’s creation of the world, where he emerged from the primal waters of chaos and brought order to the universe.
- The story of Ra’s sacred boat, which carried him across the sky and through the underworld, symbolizing the cyclical nature of life and death.
These ra myths and legends amazed the ancient Egyptians. They still captivate us today. They show the deep respect and awe the egyptian gods had for Ra, the sun god.
Anubis: The Jackal-Headed God of the Afterlife
In the ancient world of Egyptian gods, Anubis was a standout. He was known for his jackal-like head and was the god of the afterlife. Anubis was seen as the protector of the dead, guiding them through the underworld.
Anubis played a key role in Egyptian beliefs. He was in charge of mummification, making sure the dead were properly preserved. This was crucial because the Egyptians believed the soul needed the body to return after death.
But Anubis’ role went beyond just the dead. He was also the god of cemeteries and protected graves. This was important in a culture that honored the dead and believed in eternal life.
The stories about Anubis are as fascinating as the god himself. In Egyptian mythology, he weighed souls against Ma’at’s feather. This “Weighing of the Heart” decided if a soul could rest eternally or not.
Anubis’ lasting impact shows the power of Egyptian gods on us today. Even now, his story captivates and inspires. It reminds us of the deep mysteries and beliefs of ancient Egypt.
Discover The Egyptian Frequency That Transforms You Into A Wealth Magnet—In Just 24 Hours!
Isis: The Goddess of Motherhood and Magic
In ancient Egyptian mythology, Isis is a standout figure. She was the goddess of motherhood, fertility, and magic. Her role was key in shaping Egyptian beliefs and practices.
The Role of Isis in Egyptian Mythology
Isis was a top deity in the Egyptian pantheon. She was known for her healing, protection, and resurrection powers. She was also a symbol of strength, wisdom, and motherhood.
Isis and the Osiris Myth
The famous Isis and Osiris myth is central to her story. Osiris was killed by his brother, Set. Isis, filled with love and devotion, set out to bring Osiris back to life.
With her magic, Isis managed to resurrect Osiris. Together, they had a child named Horus. Horus would later avenge his father’s death and rule Egypt.
The Isis and Osiris myth has amazed people for centuries. It shows the power of love, resilience, and good overcoming evil in Egyptian mythology.
The Surprising Way To Manifest More Money Now
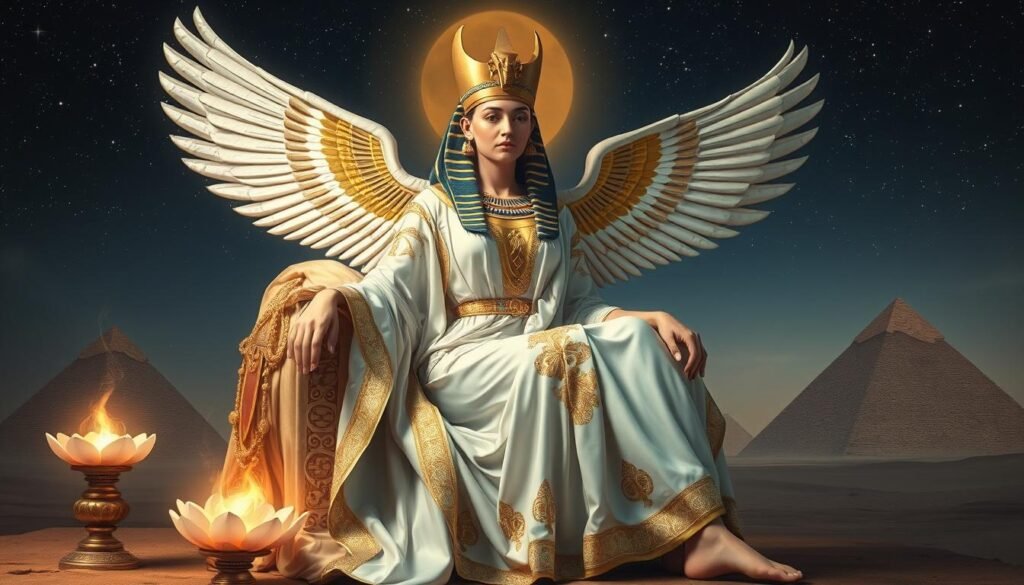

“Isis was the most powerful of all the Egyptian gods. She was the goddess of magic, motherhood, and fertility, and her cult was one of the most important in ancient Egypt.”
Horus: The Falcon-Headed God of the Sky
Horus, the falcon-headed god, is a key figure in Egyptian mythology. He was seen as the protector of the sky and the ruler of the heavens. His role was crucial in the ancient Egyptian belief system.
Horus and His Battle with Set
The battle between Horus and Set is a famous story in Egyptian mythology. Set, the god of chaos, wanted to take over Egypt. Horus, the rightful king, fought against him to save Egypt.
This fight shows the power of the Egyptian gods. Horus stood for order and justice. Set represented chaos and disorder. Their battle was a clash of good and evil.
This epic battle shaped the beliefs of ancient Egyptians. It also left a lasting impact on humanity. It has inspired many stories and artworks over the years.
“The falcon-headed Horus, with his piercing gaze, stood as a symbol of the sky’s dominion, a protector of the rightful order in the land of the Nile.”
Horus’s victory brought peace and stability to Egypt. It made Horus a vital part of Egyptian mythology. His story continues to fascinate people today, showing the lasting impact of Egyptian gods on our culture.
Osiris: The Lord of the Underworld
Osiris is a key figure in Egyptian mythology. His story is about life, death, and coming back to life. As the ruler of the underworld, he guided souls to their eternal journey.
The Myth of Osiris and His Resurrection
The story of Osiris is filled with betrayal, tragedy, and hope. Osiris was the rightful king of Egypt. But his brother, Set, was jealous and killed him.
Isis, Osiris’ wife, worked hard to bring him back to life. She used her magic to resurrect him. This made him the ruler of the underworld and the judge of the dead.
“Osiris is not a god, he is the resurrection itself.” – Plutarch, Greek historian
The myth of Osiris shows the power of death in Egyptian beliefs. It teaches that death is just the start of a new journey. This legend still fascinates many, giving us a peek into Egyptian mythology.
Install This 5000 Year Old ‘Egyptian Frequency’ In Your Brain To Manifest Money Effortlessly Like The Top 0.1% In 2024
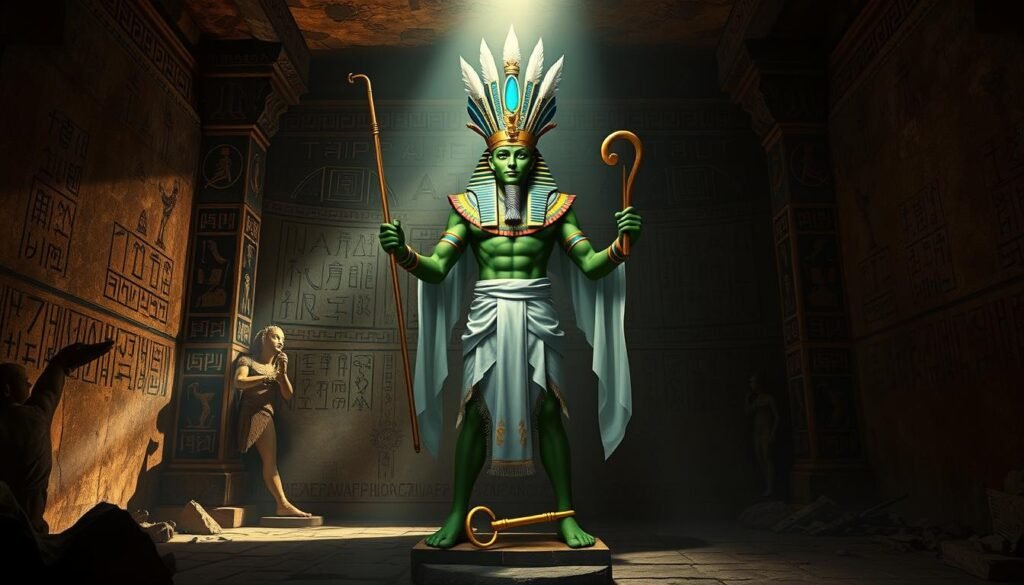

Ptah: The Creator God of Ancient Memphis
Ptah was a key figure in ancient Egyptian mythology. He was the creator god of Memphis. People revered him for his role in creating the world and his connection to crafts and professions.
Ptah was seen as the universe’s architect. He brought the world into being with his thoughts and words. He was often shown as a mummified figure, showing his role in creation and the afterlife.
Ptah was also the god of craftsmen and artisans. He was the patron of architects, builders, and metalworkers. His temple in Memphis was a place where skilled workers came to worship and improve their crafts.
Ptah was also linked to the ptah, the divine plan or blueprint of the universe. This idea of Ptah as the creator of the cosmos and the overseer of the ptah was key to the egyptian gods in ancient Memphis.
“Ptah, the Great, the Creator, who fashioned the gods, the father of the beginning, the creator of the destiny.” – from the Shabaka Stone, an ancient Egyptian text
Ptah’s legacy lives on in ancient Egyptian temples, sculptures, and inscriptions. He was a god of creation and skilled craftsmanship. Ptah is a fascinating figure in the world of egyptian gods and their impact on ancient times.
Egyptian Gods Family Tree: Unraveling the Divine Lineage
The Egyptian gods’ family tree is a complex web of relationships. It shows the hierarchy and connections among these powerful deities. This tree gives us insights into the ancient Egyptian worldview and the roles of each god and goddess.
At the center of the Egyptian gods family tree is Ra, the sun god. He is the father of many major gods, including Osiris, Isis, and Horus. The tree also shows the marriages and children of these deities, revealing the complex family bonds in Egyptian mythology.
| Egyptian God | Relationship | Offspring |
|---|---|---|
| Ra | Progenitor | Osiris, Isis, Horus |
| Osiris | Husband of Isis | Horus |
| Isis | Wife of Osiris | Horus |
| Horus | Son of Osiris and Isis | N/A |
By exploring the egyptian gods family tree and egyptian mythology family tree, we learn about the Egyptian pantheon’s complex nature. This knowledge deepens our respect for ancient Egypt’s rich culture. It also highlights the lasting impact of these fascinating deities.

“The Egyptian gods family tree is a tapestry of interwoven relationships, each thread representing the intricate connections that shaped the divine hierarchy of the ancient world.”
👉 You Don’t Deserve To Manifest Money
Bastet: The Feline Goddess of Protection
Bastet is a key figure in ancient Egyptian mythology. She is linked to protection, fertility, and the home. As a cat goddess, her worship reflects the Egyptians’ deep respect for cats.
The Worship of Bastet in Ancient Egypt
The city of Bubastis was Bastet’s main temple site. It was in the Nile Delta. Devotees came from everywhere to honor her and seek her protection.
Cats were sacred under Bastet’s care. The Egyptians mummified them when they died. This shows how much they valued these animals.
Bastet was more than just a protector. She was also tied to the moon, fertility, and the home. Her festivals were filled with music, dance, and gifts of bronze statues and amulets.
| Bastet’s Attributes | Significance |
|---|---|
| Feline Form | Represented the goddess’s connection to cats, revered animals in ancient Egypt |
| Solar Disk | Symbolized Bastet’s association with the sun and the moon |
| Sistrum | Musical instrument used in Bastet’s festivals and rituals |
Bastet, the egyptian gods feline goddess of protection, still fascinates many today. She offers a peek into ancient Egyptian mythology and beliefs.
“The cat was sacred to Bastet, the goddess of protection, fertility, and the home. Cats were mummified and buried with their owners, and the killing of a cat, even accidentally, was severely punished.”
Khnum: The Ram-Headed God of Creation
In the world of Egyptian gods, Khnum is a standout. He’s known as the ram-headed god of creation. People believed he formed human bodies on a potter’s wheel.
The khnum deity was key in the Egyptian pantheon. He was linked to creating life. Legends say he molded bodies from clay and breathed life into them, shaping their destiny.
Khnum was also tied to the Nile River. He was seen as the guardian of the river’s sources and the controller of its floods. This connection to the Nile made him even more important in Egyptian culture.
| Attributes of Khnum | Significance |
|---|---|
| Ram-headed Appearance | Representing strength, virility, and the cycle of life and death |
| Association with the Nile River | Guarding the river’s sources and controlling its floods, crucial for agricultural prosperity |
| Role as the Creator God | Believed to mold human bodies on a potter’s wheel and breathe life into them |
The worship of Khnum was mainly in Elephantine. But his influence grew, making him a major figure in Egyptian gods.
“Khnum, the divine potter, who has fashioned men and who fashions the gods.”
Khnum’s role in creation and his link to the Nile have made him a key part of Egyptian mythology.
The Significance of Animal Symbolism in Egyptian Mythology
In the world of Egyptian mythology, animals were very important. The ancient Egyptians thought certain animals had special qualities. They believed these qualities were found in their gods, who often had animal features.
This mix of egyptian gods and animals is fascinating. It shows the depth of their beliefs.
Understanding the Animal-Headed Deities
The ancient Egyptians loved many animals, like the falcon and the jackal. They used these animals to create their gods. These gods had powers and abilities from their animal forms.
- The falcon-headed Horus, the god of the sky, had the strength and vision of a falcon.
- Anubis, the jackal-headed god of the afterlife, had the sharp senses and protective role of a jackal.
- Bastet, the feline goddess of protection, was known for the cat’s grace and nurturing qualities.
These animal-headed gods connected the earthly and divine worlds. They helped the ancient Egyptians understand the natural and supernatural. By honoring these gods, they sought to tap into the wisdom of the animal kingdom.
“The ancient Egyptians saw the divine in the natural world, and they incorporated the essence of animals into their pantheon of gods.”
The Egyptians believed their gods were connected to the natural world. They saw their gods as more than just human figures. They were the forces that shaped their reality. This view of the divine and natural is a key part of Egyptian mythology.
Install This 5000 Year Old ‘Egyptian Frequency’ In Your Brain To Manifest Money Effortlessly Like The Top 0.1% In 2024
The Role of Egyptian Gods in Daily Life
The ancient Egyptians deeply respected their gods and goddesses. They built temples, performed rituals, and made offerings to keep their society balanced. These actions were not just worship but essential for their way of life.
Temples, Rituals, and Offerings
Grand temples across Egypt were dedicated to different gods. These temples were centers of religious and cultural life. Egyptians would pray, sing hymns, and make sacrifices to please the gods.
Every household had shrines, showing the gods’ presence everywhere. They guided the Egyptians’ decisions and shaped their lives.
Making offerings to the gods was a big part of daily life. Egyptians gave gifts like food, animals, metals, and art. They did this to honor the gods and keep peace between humans and gods.
FAQ
What are the most important Egyptian gods and goddesses?
Key Egyptian gods include Ra, the sun god, and Anubis, the jackal-headed god of the afterlife. Isis, the goddess of motherhood and magic, is also important. Horus, the falcon-headed god of the sky, and Osiris, the lord of the underworld, are crucial. Ptah, the creator god of Memphis, and Bastet, the feline goddess of protection, are also significant. Lastly, Khnum, the ram-headed god of creation, holds a special place.
What is the significance of animal symbolism in Egyptian mythology?
Animal symbolism was vital in ancient Egyptian mythology. Gods like Anubis (jackal), Horus (falcon), and Khnum (ram) showed the connection between gods and nature. These figures carried specific meanings that were key to Egyptian beliefs.
How did the Egyptian gods influence the daily lives of the people?
The gods and goddesses were central to the daily lives of ancient Egyptians. They were honored through temple rituals, offerings, and practices. These activities aimed to ensure the well-being of people and the kingdom’s prosperity. Egyptians sought harmony with the deities through these religious acts.
What is the significance of the Osiris myth in Egyptian mythology?
The Osiris myth is a core story in Egyptian mythology. It tells of Osiris’s death and rebirth, symbolizing life, death, and rebirth. This myth was tied to the afterlife belief. The story of Osiris, Isis, and Horus shaped the Egyptians’ view of the world and the divine.
Can you explain the Egyptian gods family tree and their relationships?
The Egyptian pantheon had complex family ties and relationships. Ra was seen as the gods’ father. Isis and Osiris, siblings and partners, had a son, Horus. Horus played a key role in the battle against Set. Knowing these family connections helps understand ancient Egyptian beliefs.